Frame houses have long and firmly seized a significant part of the private housing market in developed countries (up to 80% in America, up to 60% in Northern Europe and up to 45% in Japan). Among Russian developers, the idea of leaving the bustling city and settling in the lap of nature, without spending an astronomical sum and a couple of years of life for a magical movement, looks more and more attractive. Looking back on the long-term experience of foreign homeowners, they come to the conclusion that building only from classical materials is an outdated strategy based on traditional notions of quality.

For centuries, the best houses were considered stone and wooden buildings, good and almost eternal ; if you think there were no alternatives, other materials were not suitable for them. But the development of scientific knowledge has made our lives more multifaceted. In the past 50 years, new technologies have appeared in construction, based on new materials and breaking stereotypes about a warm house. Among them - the technology of frame-panel houses, reliable, efficient and economical.
About frame technology
According to the statistics of the UK Timber Frame Association, over the past 10 years, at least 70% of the population of Western European countries have chosen a frame technology in order to build their house. Professional builders distinguish several directions in frame housing construction:
-
Half-timbered (frame-frame technology). The oldest of all, but not lost popularity. A massive timber assembled in the form of sections with inclined beams is used as a frame. Chip wall structures - the space between the beams is filled with a suitable material, and the beams are visible from the outside of the wall.

-
Panel house . An inexpensive kind of frame technology. Such buildings are designed for seasonal use; in the summer they are comfortable, but in winter they will have to spend money on heating. The frame construction is assembled from boards and sheathed with plywood (often clapboard). Then it is the turn of laying the insulation (it is separated from the walls by waterproofing), at the end the second surface is sewn up.
-
Frame house . The basis of the building is a frame of beams and ceilings; It can be made of wood or metal. When the frame is ready, external and internal panels (OSB or DSP) are attached to it. Insulated insulation is laid between the panels, the lining is made with any finishing material. For the sheathing, not only OSB-plates can be used, but also other options: wind-shelter panels or the most well-known type - CIP-panels.
-
SIP technology . When talking about frame constructions, they most often talk about the construction of a residential building using CIP panels (another name is Canadian technology, which is not entirely accurate, since the panels were invented in the USA). The frame is sheathed with finished insulated panels (three-layer structure of factory production: insulation between the two plates).

-
Frame-panel housing construction . The frame, as in the previous versions, is absent; factory-made wall panels assume its role.
Frame-panel housing construction: types of technology
The idea to make walls in advance, in factory conditions, and only to put them together on a building site, was undoubtedly progressive. High readiness panels are assembled in the workshop, under the roof, so that their quality does not suffer. They are supplied not only with insulation, but also with facade and interior decoration, and often doors and double-glazed windows are installed in them. In Europe and America, about 20% of private frame dwellings are built using frame-panel technology; It has its own characteristics in different regions and is divided into several varieties.

North American version (not to be confused with SIP technology)
It is rather a partly panel technology, since only 15% of the elements of the house are manufactured industrially. The remaining 85% are collected at the construction site. The finished elements are wooden or metal frame, one side of which is sheathed by an OSP-plate with a layer of insulation. The builders assemble the frame, lay insulation, and then sew up the outer side.
Scandinavian technology
If, according to Canadian technology, wall blanks are used for construction, then Scandinavian - external walls assembled entirely in the workshop: The frame is sheathed by OSB-plates from two sides, heat insulation material is placed between the plates .Also in the factory installed double-glazed windows and doors. The workers need only to assemble the outer panels together and sheathe them. Internal walls are assembled in the usual way (directly at the construction site).

On our site you can familiarize yourself with the most popular projects. houses on panel-frame technology from construction companies represented at the exhibition of houses "Low-rise Country".
Central European technology
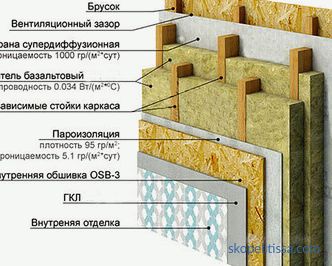
The most technological production with minimal use of manual labor is known to us as German technology. All elements are assembled on an automated line, which, together with the control of each stage, ensures a high quality house set. In factory conditions not only panels of external walls and partitions are made, but also elements of floors and roofs. The panel includes:
-
Base - wooden frame made of beams. For its plating using a variety of plate materials: moisture-resistant OSB-and DSP-plates, drywall and fibreboard. The design involves the installation of corrugated pipes for wiring, podozetnikov, drilling holes for ventilation and sewage; sometimes (on request) windows and doors are installed.
-
Thermal insulation . Used mineral wool, basalt or ecowool, polystyrene foam and other insulation.
-
Protection . Paro-and moisture-proof films provide moisture resistance design.
-
Fasteners . Metal fasteners are used, thanks to which the panels are connected with high precision and reliability.
-
Finishing . For exterior cladding, lining, siding, ceramic plates and a blockhouse are used. When finishing with decorative plaster, the panels are pre-lined with cork or fiber boards.
A domokomplekt is delivered to the construction site, which includes:
-
wall structures with tightly fitting components;
-
floor slabs;
-
truss system (or truss trusses).
Lifting equipment is used to deliver the housing set and install the house. The elements are mounted in a single structure on a previously prepared foundation, then it is the turn of roofing, interior and exterior (if necessary), and laying of utilities.

Advantages and disadvantages of frame-panel technology
Panel-frame houses according to German technology have a number of undeniable advantages:
-
Quality . Work on an automated production line minimizes the likelihood of errors and ensures high accuracy in the manufacture of parts. Since the processes are controlled by a computer, the details of the house correspond exactly to the approved design drawings. The structure is durable, easily copes with loads (even with an earthquake).
-
Standardization . German thoroughness and maniacal love for precision reflected in the approach to the production of prefabricated houses. During the process, all norms and requirements are strictly followed, and the project documentation is processed using a specialized software package. Debugged production guarantees ease of installation and further maintenance-free operation.
About how houses are built using Canadian technology in the following video:
-
High construction speed . You do not have to spend a dozen years in a state of permanent construction. The division of labor and the use of a crane makes the construction of a house a quick and smooth process. The assembly of a small one-story cottage takes 2-4 days, the installation of an average project takes 10-14 days.
-
Savings in construction . Instead of the usual truss system, truss trusses can be used, which will speed up the assembly and save up to 40% of the budget allocated for the arrangement of the roof.
-
Independence from the weather . Although wood of chamber drying is used for the framework (with a humidity of 15–18%), its quality will not improve its wetness, and therefore is undesirable. Knowing that the construction of the cottage will take no more than two weeks, it is possible to plan the construction for a dry period. When using the classic frame technology (with insulation on the construction site), the risk of wetting and deterioration of the insulating material is much higher.

It can be interesting! In the article on the following link read about home from a mini-bar.
-
High quality home . It is a consequence of the ideal geometry of wall panels (permissible deviation - 1-3 mm). Such a house will always be warm, the floor will not creak and the chandelier will not shake.
-
Operating savings . Energy efficiency prefab house saves money on heating.
The disadvantages of the method are:
-
The impossibility of adjusting . Such a project is considered typical, in contrast to other frame technologies; It is impossible to make changes and modifications during construction (or it is very difficult and therefore costly).
-
Price . Factory panels are more expensive than the framework mounted on a building site, for 15-20%. Despite the highest cost (among frame technologies) cost, this method is the most rational in terms of price / quality. In terms of performance, it is comparable to a more expensive half-timbered building.
-
Use of lifting equipment . Part of the cost, without which it can not do.
About modular high-availability frame houses in the following video:
-
Need ventilation . Steam and waterproofing do not allow air to circulate freely through walls (as in wooden buildings), forced ventilation is needed.
-
Flammability . Frame technology refers to the wooden housing construction, so all the wooden parts are necessarily treated with flame retardant.
Architectural constraints
Prefabricated frame projects usually have a simple architectural solution, in which you can see both their advantage and their disadvantage. Most of these houses are simple, their elements have simple strict forms. Due to the rejection of external delights, an optimal price / quality ratio is achieved.

Most companies prefer to work on standard projects (sometimes with the adaptation of the project to the needs of the customer). Some are also engaged in individual design, but they should not look for houses with complex facades, curved or multi-layered surfaces and other excesses. Despite such restrictions on the shape, the facade can be styled in another way, turning it with the help of decoration into an elegant brick or cant structure. If prudently laid a sufficient width of the foundation, the walls can be lined with clinker (or ordinary) brick.
Restrictions exist in the size of rooms. The parameters of the premises are limited by the distance between the uprights of the frame, and from different manufacturers can be 4-10 m (with a ceiling height of 3 m). If you want more spacious rooms, they will have to be assembled from two (or more) modules, the joining of which can break the style (if you cannot successfully beat or hide it in the walls).
About the installation of the German frame-panel house in the following video:
It might be interesting! In the article next link read about the technology of construction of high-rise housing in private housing.
Possible consequences of buying low-quality panels
It may happen that a manufacturing company declares a quality that, to put it mildly, does not correspond to the real one. Outdated equipment, unqualified personnel and the use of non-certified materials significantly reduces not only the cost, but also the quality of the finished prefab house. The consequence of using low-quality panels can be:
-
Formation of cold bridges . Occurs if the panels are assembled inaccurately and after assembly, gaps remain between them, covered only by the finish. You can forget about saving on heating.
-
Violation of the geometry of the structure . If the discrepancies in dimensions exceed 3-4 mm, the overlap lags may take different heights. From the squeak of the floor you will not get rid of.
To minimize such troubles, you should contact companies with an impeccable reputation and high standards. Maybe their prices for construction will look somewhat higher than that of one-day firms, but in the long run the costs always pay off, because a poorly made house will constantly require new financial investments for repairs. The work of specialists is preferable for many reasons, and you can recognize a serious organization by the following features:
-
They work on modern equipment and regularly train personnel.
-
Often, a full production cycle is established: for the frame and wall panels of the future house, high-quality wood is used, which is dried and processed.

-
Use certified building materials .
-
Make up a contract with the customer in which warranty obligations are written.
-
Attach an estimate of to the contract with a complete list of materials and works, with transparent calculations. You will know not only the total amount, but also the cost of each stage.
-
Do not violate the technological requirements and control the quality, which ensures reliable operation of housing.
-
A house is rented to the customer that meets all requirements of the SNiP.
When placing an order for house set using frame-panel technology, you will not be able to evaluate the filling of the panel structure, the quality of thermal insulation, steam and moisture protection. When choosing a company, pay attention to such that:
-
Allows you to visit production to see with your own eyes how the walls of the house are assembled. If you do not have the opportunity to get to the factory, the company will make a video of all stages of production.

-
Give a guarantee for house set for 5-10 years.
Care should be taken of construction organizations that:
-
Immediately, without prior estimation, call the construction cost . Usually all risks are invested in such an amount, but not all stages for which you have to pay extra.
-
They offer an attractive price, far below the market . A common variant of fraud among scam builders. In the midst of the works, you are informed that some work (for example, wiring communications) are not included in the price, and an additional charge is needed. The horses at the crossing do not change, and for all subsequent conditions you will have to agree. As a result, the house will be built and, perhaps, its quality will suit you, but the price will be much higher than the market.
Projects and prices of country houses
Among all existing technologies and prices, frame-panel houses are the most pleased with the construction speed and excellent quality. German technology does not require the development of drawings, selection and purchase of building materials from the customer. The factory kit enters the construction site fully equipped; the cottage is being built before our eyes, within 2-3 days.

The limited architectural solutions are compensated by a large selection of finishing technologies, thanks to which even the box can turn into an aesthetically perfect structure. Very often, the decoration of such projects is the use of glazing - panoramic windows look advantageous in country cottages in the style of minimalism or high-tech. The average price of country houses, built on a turnkey frame-panel technology (in the Moscow region), ranges from:
-
Houses to 100 m 2 : 1.7-2.4 million rubles.
-
By an area from 100 to 200 m 2 : 2.8-3.95 million rubles.
-
From 200 to 300 m 2 : 3.9-5.45 million rubles.
It might be interesting! In the article on the following link read about the Norwegian technology of houses from the mast.
Conclusion
All frame constructions can be considered as energy efficient. Describing the frame-panel housing, you can safely add two more epithets - pre-fabricated and high-quality. Such a proven method of rapid erection, originally designed for use in cold and snowy winters, confidently wins a place in the sun on the vast Russian expanses.




