The main cause of concrete destruction is water. Durable reliable monolith under the influence of moisture loses its properties. The liquid, penetrating into the porous heterogeneous structure of the stone, washes away the components of the cement binder, causes corrosion of the reinforcement and mortar. Density and frost resistance decreases, destructive changes appear - cracks, chips, cavities.

How concrete is destroyed
If access to the foundation is available chills, repeated repeated freeze-thaw cycles provoke rupture of bonds in the concrete structure. Destruction happens very quickly. Penetrating deeper into the body of the monolith, the water, turning into ice, contributes to the further disclosure of cracks.
Through-filtration in the body of the foundation leads to the moistening of the structures supported on it. As a rule, these are walls made of porous materials with high insulating qualities. Constant dampness impairs their properties, causes the appearance of mold fungi, spots, salt stains. In the area of particular risk - basements, basement and first floor. Increased humidity adversely affects the microclimate of the premises, interior decoration.
Steel reinforcement is very sensitive to the wetting of concrete. Metal under the influence of water and substances dissolved in it passes into the form of oxides and salts with increasing volume. In the electrolyte, because of the potential difference between the sites, stray currents arise. As a result, the steel structure is subjected to electrochemical corrosion, destroying the remnants of the reinforcement cage.

The bearing capacity of the foundation is reduced, which means a high risk of deformations and destruction of the elevated part of the building.
Waterproofing the foundation slab is an important component of the foundation construction work. It will help to avoid the negative effects of moisture in the body of concrete.
Baseline waterproofing rules for foundations
High groundwater levels, rainwater and flood moisture, and occasional drains result in wetting of the concrete structure. The composition of the liquid may include corrosive substances - salts, alkalis, acids that cause corrosion of concrete. Selection of measures for waterproofing foundations regulates SNiP 2-03-11-85.
Effective protective measures are carried out at the design and construction stage. They include:
- Operations for the selection of the optimal composition of the concrete mixture, taking into account the brand of moisture resistance and the category of crack resistance.
- Constructive solutions that lead to the restriction of direct contact with water (drainage device).
- Protection of reinforcement with a layer of at least 45 mm.
- Compaction of fresh mortar with vibrators.
- Surface treatment with waterproofing materials.
- Creating hydrobarriers.
On our site you can find contacts of construction companies that offer design services and repair of the foundation. Directly to communicate with representatives, you can visit the exhibition of houses "Low-rise Country".
Waterproofing is designed taking into account the type of soil and the nature of moisture - the presence of backwater from high groundwater table, underground rivers, slopes, environmental aggressiveness, reagent composition. The brand of concrete is waterproofed according to the number of floors of a building, material and method of construction:
- for panel board or frame houses up to three floors high - W4;
- from timber or W4 logs on weakly lousy, W6 on heaving soils;
- for houses made of gas, foam or expanded clay concrete - W6 and W8;
- for brick or monolithic - W8.
The optimum water-cement ratio ensuring the brand water-tightness of concrete is 0.4. To reduce the stiffness of the mixture, plasticizers are added. Apply also clogging and hydrophobic additives.
For slab foundations, concrete with frost resistance F 35 ... 75 is used. 75. The content of clay particles in sand and rubble over 1% is not allowed. When preparing the mixture, the water-cement ratio is minimal, since the liquid solution after hardening tends to form shrinkage cracks.
Gaps in the formwork leading to leakage of cement milk and reduction of brand characteristics are not allowed.
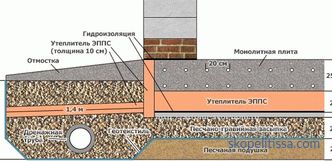
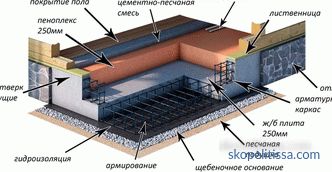
Construction of the base plate
The base plate is a structure made of layers of hydro and thermal insulation, reinforcement, concrete, laid on a flat compacted base. Drip materials are crushed stone, gravel, coarse sand.
The location mark is determined depending on the type of soil, the normative freezing depth, the groundwater level, the load from the building, the presence of a basement or basement in the project.
It is recommended to lay under frame or lumber houses on clay soils with high groundwater table foundations to a depth of 0.5 m. On sand with low water levels, the slab is deepened according to the draft without restrictions.
On heaving or highly compressible soils with deep freezing, close to GWL, located under the structure of underground lakes and water layers, it is recommended to build a slab on piles. This is a combined construction, where 85% of the load perceives vertical freestanding supports, 15% - the flat part of the foundation.
Experienced builders are advised not to arrange basements and basements at high groundwater levels. No matter how reliable waterproofing, water will find even the smallest gap. It threatens to leakage, dampness and endless repairs.
Waterproofing methods
Foundation slab waterproofing is carried out using a set of measures aimed at reducing contact with moisture by removing it from the surface of the structure, giving the soil waterproof properties by applying a protective layer.
Among the main protective design measures:
- The design of the drainage system. The purpose of the work - the collection and disposal of groundwater, snowmelt and rainwater in areas with frequent flooding, high rainfall. The design of perforated pipes is connected to wells, reservoirs or sewers. When the water level rises, excess moisture by gravity or by means of pumps is removed from the zone adjacent to the foundation.
- Replacing the soil with non-cracking materials. This is a mandatory operation on all types of soils, except sandy or coarse, with a low GWL. The remaining bases, whose share in our country exceeds 80%, are subjected to excavation and replacement with crushed stone, gravel and sand. The thickness of bedding is from 30 cm. Such a measure reduces the heaving and prevents the layer of earth from protruding towards the plate.
- Ground stabilization. When stabilizing the soil, their bearing capacity, water resistance, stability, strength and erosion resistance increase. Amelioration is carried out by injecting binding solutions, by exposure to electric or temperature fields. According to the method of operation used, they are called cementation, bituminization, silicatization, electromelting, and artificial freezing. In this way, sand, loess, quicksand, slopes are fixed.
- Device cold seams. When pouring a large amount of concrete with a break of more than 5 hours, a weakened area is formed at the place where the layers overlap. Subsequently, water seeps through the microcracks. To prevent this from happening, the joint zone is projected in advance, filled with a waterproofing key and continues to be concreted. This type of protection is used when installing the foundation of monolithic or precast concrete, for example, road slabs.
Conducting these activities reduces the water saturation of the environment, the aggressiveness of the effects of substances on the structure, gives it solidity. To prevent moisture from entering the concrete body, various types of surface waterproofing are used. These materials are impermeable to water or impart hydrophobic properties.
Types of waterproofing for slab foundations
Waterproofing of the foundation is not necessary if:
- the house stands on a hill;
- at a distance from water bodies;
- low GWL (more than 2 m);
- the soil under the base is sandy, rocky, coarse without clay;
- The climate of the region is not rich with rains and snow;
- a layer of non-metallic materials is poured under the base plate;
- drainage is laid;
- along the perimeter there is a blind area with storm drainage for collecting and draining rainwater.
In this case, the theoretical probability of moisture getting under the slab is zero. But such cases in real life are rare. Therefore, the waterproofing of the slab foundation is a prerequisite for maintaining the durability of the structure under any circumstances.
It may be interesting! In the article on the following link read about the waterproofing of TechnoNIKOL.
Rolled insulation, membranes
Protection against damping of the lower horizontal surface is carried out by laying insulating membranes or rolled materials under the base of the slab with sizing or welding of the joints. Apply:
- polymer films;
- profiled membranes;
- bentonite mats;
- ruberoid;
- Stekloizol;
- Linocre;
- Uniflex.

The surface is pre-coated with a primer, the panels are laid with an overlap of at least 20 cm.
Surfacing, sprayed waterproofing
The foundation slab for concrete preparation is protected with weld insulators.The cement screed is applied using special burners:
- Hydroplast;
- Bicrost;
- Technoelast;
- BOM;
- Gidroizol.

The formwork is mounted on the prepared surface, the reinforcement cage is laid, the design thickness plate is poured.
A high-quality waterproofing film is produced by spraying liquid rubber using a special apparatus under pressure. Thickness of 2-3 mm provides water resistance at the level of roofing material or other rolled material pasted in several layers.
Sprayers, impregnations
Coating materials are applied in several layers. These are:
- polymer emulsion;
- bitumen mastic;
- liquid rubber;
- resins and pastes.
Such a coating is easy to do with your own hands.

Impregnation is called penetrating waterproofing. Once in the pores and capillaries of the concrete, the solutions crystallize and prevent the filtration of moisture. The depth of the protective layer reaches 7-12 cm. Domestic manufacturers produce:
- Penetron;
- Hydrochitis;
- Lakhta;
- Osmosis;
- CT Tron.
Impregnations should be applied quickly, it is not allowed to re-dilute with water.
Insulation of technological holes
During the excavation work in the underlying layers, the places for the supply of communications are prepared. Before pouring concrete into the formwork, a sleeve is placed - a piece of steel or asbestos-cement pipe of a larger diameter than the entrance main. So that water does not penetrate through the boundaries of the technological opening, they are carefully isolated with ready-sealed bushings. They are convenient to use. Available collapsible and non-collapsible design.
It might be interesting! In the article on the following link read about waterproofing a well from concrete rings.
Total
Waterproofing of the foundation slab is an important part of general construction works. The durability of the foundation and the building as a whole depends on the quality of materials and compliance with the technology. Do not ignore this stage of construction, it is best to entrust it to professionals.




