After the introduction of a new standard for thermal protection of buildings, insulation has become relevant even for those houses that were previously considered "safe". Owners of old buildings can do nothing, but you have to be prepared to pay growing energy bills. And the projects of new houses will not be approved if they do not meet the requirements of SNiP 23-02-2003. There are several technologies that provide regulatory indicators for buildings of any materials. The main thing is to choose the insulation for the walls of the house outside in each case.

Why external insulation, but not internally
The most understandable argument for a non-expert sounds very convincingly, although this is a secondary factor - the insulation from the inside "takes away" the useful volume of residential and office space.
Builders are guided by the standard, according to which the heat insulation must be external (SP 23-101-2004). Warming from the inside is not directly prohibited, but it can only be done in exceptional cases. For example, when work outside is impossible to carry out due to the design features or the facade "belongs" to the house, which belongs to the architectural monuments.
The result of proper internal warming of the house on the video:
Internal wall insulation is allowed provided that a durable and continuous vapor-proof layer is created on the side of the room. But this is not easy to do, and if warm air with water vapor enters the insulation or on the surface of a cold wall, the appearance of condensate is inevitable. And the culprit is the "dew point", which will move either inside the layer of insulation material, or on the border between it and the wall.

That is, deciding how to properly insulate the house, in most cases, the answer will be based on clear regulatory recommendations - from the outside.
Popular heat-insulating materials
From the large list of heat-insulating materials it is possible to select several of the most popular and those that are used if the budget allows it or for other reasons. Traditionally, the popularity of materials is determined by a combination of good thermal insulation characteristics and relatively low cost.
More commonly known as "foam plastic." To be precise, apart from the plates, this material is also used in granular form as bulk insulation.
Its thermal conductivity depends on the density, but on average it is one of the lowest in its class. Thermal insulation properties are provided by a cellular structure filled with air. Popularity due to the availability, ease of installation, good indicators of compressive strength, low water absorption. That is, cheap, fairly durable (as part of the design) and not afraid of water.
Polyfoam is considered low-combustible, and with marking PSB-S it is self-extinguishing (does not sustain combustion). But in case of fire, it releases poisonous gases, and this is one of the main reasons why it cannot be used for insulation from the inside. Its second drawback is low vapor permeability, which imposes restrictions on the use of wall insulation made of "breathing" materials.

- Extruded polystyrene foam
It differs from the foam by a fundamentally different manufacturing technology, although the raw materials are all the same polystyrene granules. According to some indicators, he surpasses his "relative". It has the same percentage of water absorption (no more than 2%), on average, 20-30% lower thermal conductivity (Table D. 1 SP 23-101-2004), steam penetration is several times lower and compressive strength is higher. Thanks to this set of qualities, this is the best material for warming the foundation and the basement, that is, the walls of the basement and the "zero" floor. The disadvantages of EPPS are the same as those of foam plastic, and it costs more.

- Stone, it is basalt, wool
It is a subspecies of mineral wool, the raw material of which is rock rocks (most often basalt). A completely different type of insulation material, low thermal conductivity of which is ensured by the fibrous structure and low density. It gives in to foam plastic and EPS in thermal conductivity (on average it is 1. 5 times higher), but unlike them it does not burn or smolder (the combustibility class is NG). Refers to "breathable" materials - according to the new standard, it sounds like low "resistance to air penetration."

But there are other materials for insulation houses outside, which, although used less frequently, have their merits.
Thermal insulation materials - new products on the market
Additionally, you can always consider new options - they are a little more expensive, but often somewhat more efficient than traditional ones.
Common "domestic" polymeric material. Also well known as foam rubber for furniture (in the form of "soft" mats) or as polyurethane foam for sealing gaps. When warming it is also used in the form of slabs or sprayed insulation.
The polyurethane foam plates have low retention capacity, so it is not used in wet facade systems.
But this is a common insulating material for making sandwich panels. The same technology underlies the production of thermopanels for facade cladding. Such a panel is a heat-insulating slab with a decorative layer already applied on the plant (clinker tiles or stone chips). Two types of insulation: polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam. In the first case, the thermopanel is two-layered, in the second - a three-layer (OSB or moisture-resistant plywood is used as the carrier base). Two mounting options: on dowels / anchors (open method) or on your system of hidden fasteners.

Sprayed polyurethane foam is in demand if you need to create a seamless thermal insulation layer on complex surfaces. Until recently, there was the only technology of applying such a layer - using professional installations, working with a two-component composition (mixing occurs during spraying).

Now in Russia for domestic use there is a production of one-component PPU, which produced in an aerosol container with a capacity of 1 l. As the manufacturers assure (there are two competing companies), it is much cheaper to make 1 m2 with your own hands than when concluding an agreement with specialized enterprises using professional equipment. And this option than to insulate the house from the outside is quite attractive, if you literally lack 2-3 cm of insulation layer.

Relatively new thermal insulation material. The technology of warming the enclosing surfaces is based on cellulosic fiber material, which is applied to the walls using a special installation. There are two options for warming: filling the plane between the wall and cladding, spraying in the composition with adhesive bonding to the wall with the installed crate (and the subsequent installation of the front panels).
Of traditional materials, glass wool (a subtype of mineral wool) can be mentioned, but because of its fragility and the formation of the smallest "dust" with sharp edges during installation, it was replaced by stone wool, which is safe both during installation and operation.
The better it is to insulate a house outside - standards for the number of layers
If you follow the regulatory documents, there are two options for how to insulate a house outside by the number of construction and insulation layers: two-layer and three-layer. And in the second case, the exterior trim panels or plaster is not considered to be an independent layer, although their thermal insulation properties are taken into account. In three-layer walls, structural material acts as an external (third) layer.

In addition to this classification, there is also a division by the presence of a ventilated and non-ventilated layer .
Total: four recommended types of technical solutions for thermal protection of walls. The regulations already indicate the options for insulation depending on the materials of the wall and thermal insulation:
- brickwork, reinforced concrete (with flexible connections), expanded clay concrete - all types of solutions;
- wooden houses - enclosing structures with two-layer, three-layer walls and with a ventilated air gap;
- thin-framed frame houses - three-layer walls with thermal insulation in the middle, as well as with a ventilated and non-ventilated air gap;
- cellular concrete blocks - two-layer brick walls, and ta kzhe with ventilated or non-ventilated interlayer.
In practice, for warming low-rise buildings, such a variety of solutions comes down to the choice between a “wet” or hinged facade. Although as a thermal insulation materials consider it recommended by the standard - mineral wool or polystyrene foam (as an alternative - EPS).
But in each case there are preferences.
Clearly about the choice of how to warm the house outside on the video:
What is better to warm the house outside depending on the material of the walls
For the insulation of a brick house there are no restrictions on the choice of technology. Different options can be considered only depending on the chosen method of finishing the facade:
- Facing brick.This is a classic three-layer wall construction on flexible connections. Even using polystyrene foam, provide a ventilated air gap to weather the water vapor and prevent the wall materials from getting wet.
- Wet facade. You can use mineral wool and polystyrene foam. The first option is preferable - for ceramic bricks vapor permeability is higher than that of foam plastic. And according to clause 8. 5 SP 23-101-2004, the location of the layers should contribute to the weathering of water vapor to prevent moisture accumulation.
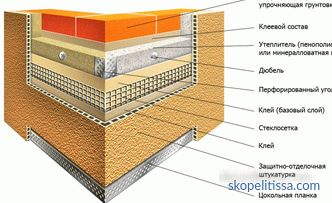
- Ventilated Facade. With cladding wall panels or large format granite on the crate. Insulation traditional for all hinged facades - mineral wool.
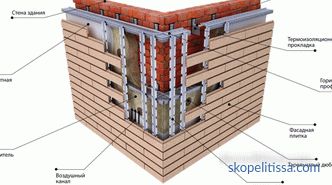
Wooden houses (log or beam) are insulated with mineral wool only on the technology of the hinged facade.
For them, you can find examples of using polystyrene foam and plaster using the wet facade method. In this case, make a ventilated gap between the wall and the plates of the foam with the help of remote obreshetki. Although this disappears the main advantage of the "wet facade" - the simplicity of design and installation.
How to calculate the thickness of the insulation
If you “look through” SP23-101-2004 or similar in content, but a later set of rules SP 50. 13330. 2012, then you can see that calculate the thickness insulation is not so simple.
Each building is "individually." When developing a project and approving it, such heat calculation is done by specialists. And here a whole set of parameters is taken into account - the region's features (temperatures, the duration of the heated season, the average number of sunny days), the type and area of the glazing of the house, the heat capacity of the floor covering, the insulation of the roof and the basement room. Even the amount of metal bonding between wall and veneer matters.
But if the owner of a previously built house decides to insulate it (and the new standards introduced in 2003 are much tougher than the old ones), then he will have to choose between three parameters of the “standard thickness” of insulation - 50, 100 and 150 mm . And there is no need for accuracy of calculations. There is such a scheme, where the equivalent dimensions of the thickness of different materials (in average form) are given, the wall of which will meet the new requirements of thermal protection.

And then simple. They take the thickness of the wall from a certain material, they look at how much is missing to the normative. And then they calculate in proportion what thickness of the insulation layer of the wall of the house outside should be added. Given that the wet facade has a layer of plaster, and the ventilated one has an air gap, plus the interior of the facade walls, you can be sure of sufficient thermal protection.
And the question of warming the roof, floors and choosing good windows is decided separately.
Even easier is to use one of the many online calculators. The figure here, of course, is approximate, but rounded up to the nearest standard thickness of insulation, it will give the desired result.
How to properly install insulation on the facade
Before installation, the facade must be prepared: clean the old finish, remove dirt and dust, dismantle the hinged elements of engineering systems, remove the ebb and peaks (you still have to change to wider), remove signs, signs and facade lights. Then the surface of the wall needs to be strengthened - to seal up the cracks and chips, clean the crumbling areas, apply a deep penetration primer.

For secure mounting of polystyrene foam or hard mineral wool mats in the system wet facade surface the walls should be as flat as the irregularities can be leveled with adhesive solution. With a height difference of up to 5 mm, the solution is applied over the entire plate of insulation, with irregularities from 5 to 20 mm - around the perimeter and in the form of "lozenges" on 40% of the surface of the plate.
The first row of plates is mounted with an emphasis on the starting bar, which also sets the horizontal level. The second and subsequent rows are placed with a vertical seam shift (not less than 200 mm), aligning the insulation surface in the area of the joints so that the height difference is not more than 3 mm. When we wall the walls around the openings, they make sure that the seams of the plates do not intersect in their corners. Each slab is additionally fixed with umbrella dowels at the rate of 5 pcs. on 1 m2.
Before applying the plaster, the surface of the plates is reinforced with fiberglass, fixed in the middle of the layer of adhesive mortar with a total thickness of 5-6 mm.
The density of polystyrene foam is chosen equal to 25-35 kg / m3.
Clearly about the mineral wool insulation on video:
Mats of mineral wool of Russian trademarks for the “wet facade” system should correspond to index 175, imported - be marked "facade" and a density above 125 kg / m3.
Warning. In the "wet facade" system, the heater is mounted only in one (!) Layer. The vertical surface of two layers of “soft” plates with a load in the form of plaster behaves unpredictably, especially with changes in temperature and humidity conditions. Do not flatter yourself with the arguments that the second layer of plates overlaps the seams of the first and eliminates the "cold bridges".
In the ventilated facade, hard mats of mineral wool with a density of 80 kg / m3 are used. If the surface of the mats is not laminated, then after they are attached to the crate, the surface is covered with either glass fiber or a vapor-permeable membrane.
The layout step of the batten is chosen 2-3 cm less than the width of the mats. In addition to attaching to the crate, the insulation is additionally fixed to the wall with dowels, umbrellas.
The size of the air gap between the insulation and lining should be in the range of 60-150 mm.
Important. Size 40 mm is normalized for non-ventilated air spaces.
To ventilate the interlayer in the lining, equip the inlets in the area of the basement and the weekend - under the eaves of the roof. The total hole area should be at least 75 cm2 per 20 m2 of wall.

As a result, is it worth it to insulate
Thermal insulation houses are a profitable investment even in the short term. Investments will quickly pay off by reducing the cost of heating and air conditioning.
Our site also presents companies that specialize in front and finishing materials , which are represented at the exhibition of Low-Rise Country houses.




